To build a Terraform workflow using GitHub Actions for Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD), you’ll set up automation to manage your Terraform infrastructure using GitHub’s CI/CD capabilities. Here’s a detailed, step-by-step guide to create this workflow.
Prerequisites
- GitHub Account (and a repository where the Terraform code is stored)
- Terraform installed
- AWS account with administrator rights.
Step 1: Create a New GitHub Repository (if needed)
If you don’t have an existing repository, create one on GitHub to store your Terraform files.
Step 2: Configure Terraform Code
Ensure that your Terraform configuration files are structured properly within your repository.
Find the code (for main.tf, outputs.tf, terraform.tfvars and variables.tf):
https://github.com/djcloudking/terraform-challenges/tree/main/15_Terraform%20workflow%20with%20Github%20Actions%20Pipeline
Step 3: Store Cloud Provider Credentials in GitHub Secrets
GitHub Actions will need access to your cloud provider’s credentials to apply the Terraform configuration. Store the cloud provider credentials in GitHub Secrets.
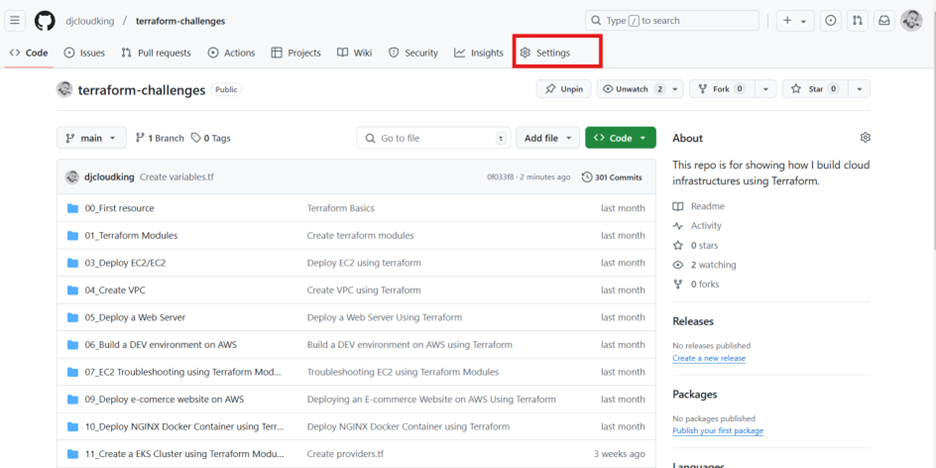
- Go to your GitHub repository.
- Navigate to Settings > Secrets and variables > Actions.
- Click New repository secret.
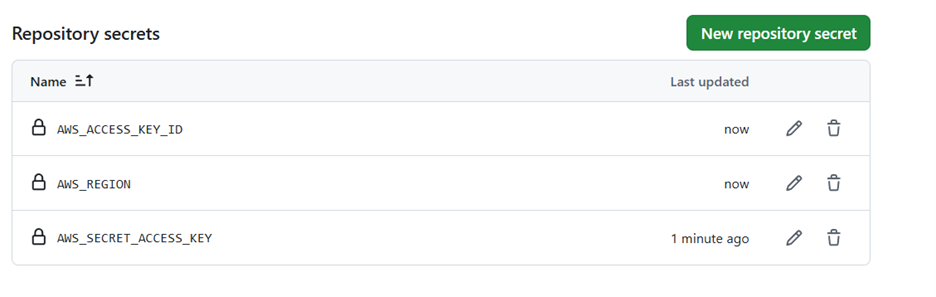
- Add the following secrets depending on your AWS cloud provider:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYAWS_REGION
Step 4: Set Up GitHub Actions Workflow File
Create a GitHub Actions workflow to automate your CI/CD pipeline.
- In your repository, navigate to the Actions tab.
- Click on New workflow.
- Choose set up a workflow yourself to create a custom workflow file.
- Create the
.github/workflows/terraform.ymlfile in the repository.
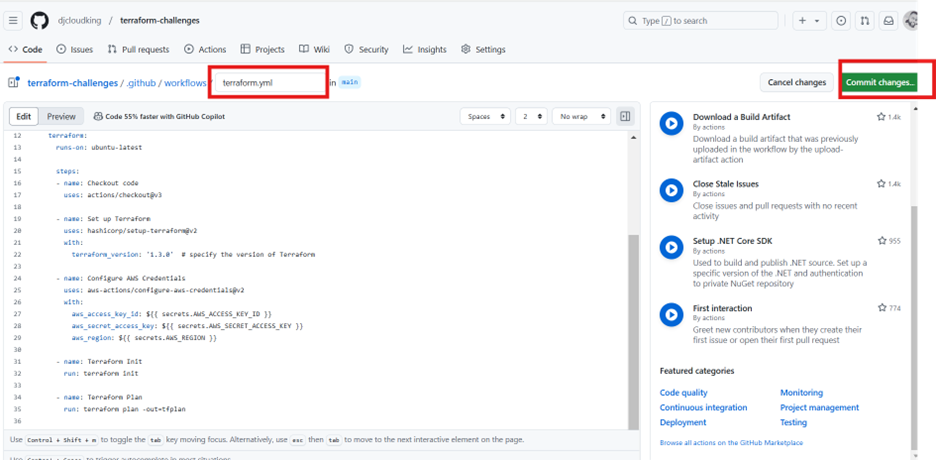
Step 5: Breakdown of the Workflow
on:section: This defines when the pipeline will trigger. In this case, the pipeline triggers onpushto themainbranch and on a pull request targeting themainbranch.jobs:section: The jobs section defines what actions are performed.- Checkout code: This step checks out the repository’s code into the GitHub runner.
- Set up Terraform: Installs Terraform and specifies the version to use.
- Configure AWS credentials: This step uses the GitHub Secrets to configure AWS credentials (or equivalent for Azure/GCP).
- Terraform Init: Initializes the Terraform project by downloading necessary providers and setting up the backend.
- Terraform Plan: Runs
terraform planto check the changes that will be made in your infrastructure. - Terraform Apply: Applies the Terraform plan to the cloud provider, creating or modifying infrastructure resources.
Step 6: Test the Workflow
- Commit and push the changes to the repository.
- Navigate to the Actions tab in your GitHub repository.
- You should see the Terraform workflow triggered by your commit. Monitor the progress of each step.
- Once the workflow completes successfully, Terraform will apply the changes to the cloud infrastructure.
Voila! You’ve build a GitHub Actions pipeline that automatically runs Terraform workflows (init, plan, and apply) whenever changes are made to the code.
This automation greatly reduces the risk of manual errors and enables fast, repeatable infrastructure deployments, enhancing the CI/CD process for managing cloud infrastructure.


Leave a Reply