In this tutorial, I will show you how to set up Docker containers for Python projects with Boto3 and bind mounts. Let’s have fun.
Scenario
A Python development team is looking to simplify their setup process and maintain consistency across environments. They can create a Dockerfile to set up Python and Boto3 environments, download repositories locally, and configure containers for seamless collaboration.
Before starting, we need few tools ready.
Prerequisites
- An AWS account
- An IDE
- Docker engine installed
- Basic understanding of Docker commands
- Familiarity with Git and GitHub
Step 1: Install Docker
- Log in to your AWS account and open CloudShell
- If Docker isn’t already installed, follow these commands:
sudo yum update -y
sudo yum install docker -y
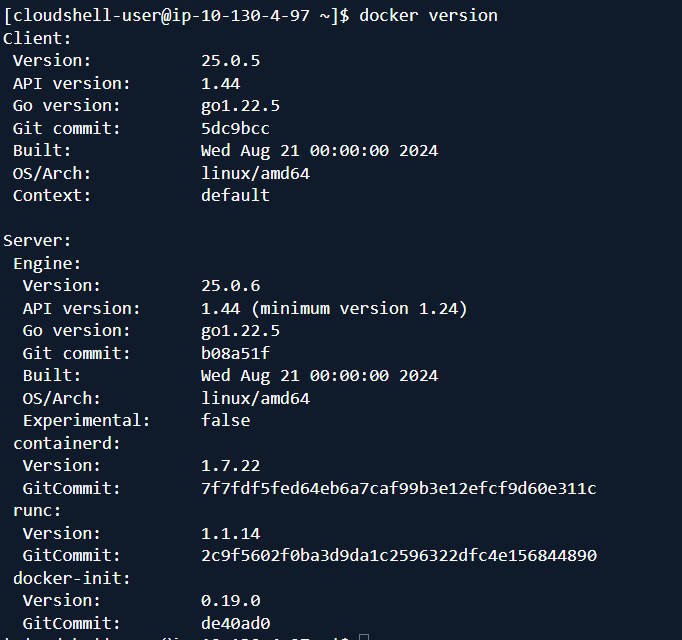
Verify the installation by checking the Docker version:
docker –version
Step 2. Create a Dockerfile and Build an Image
- Create a project directory:
mkdir dj_Docker
cd dj_Docker
- Create a Dockerfile: touch Dockerfile

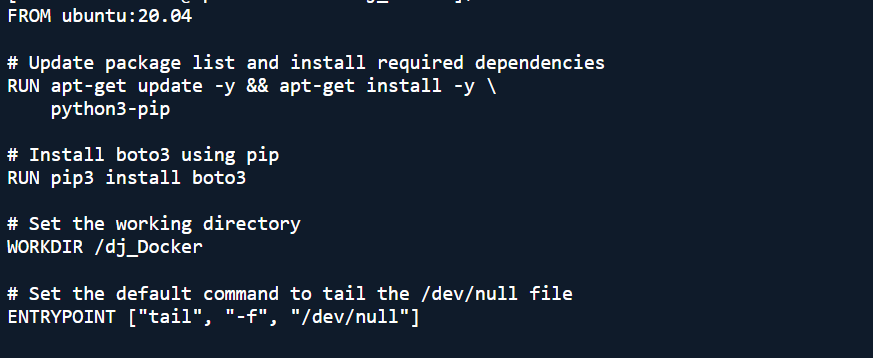
- Use the following content:
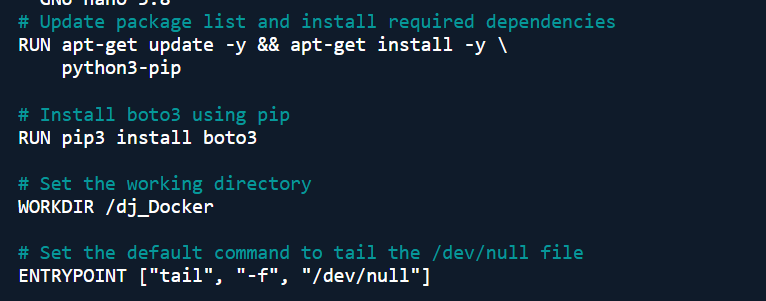
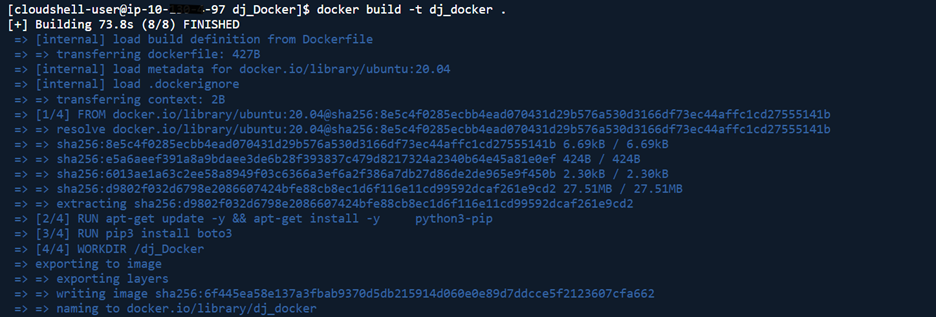
- Build the Docker image: docker build -t python_boto3_image .
Note: When running docker build, I realize I forgot to mention FROM in my dockerfile, and received this error
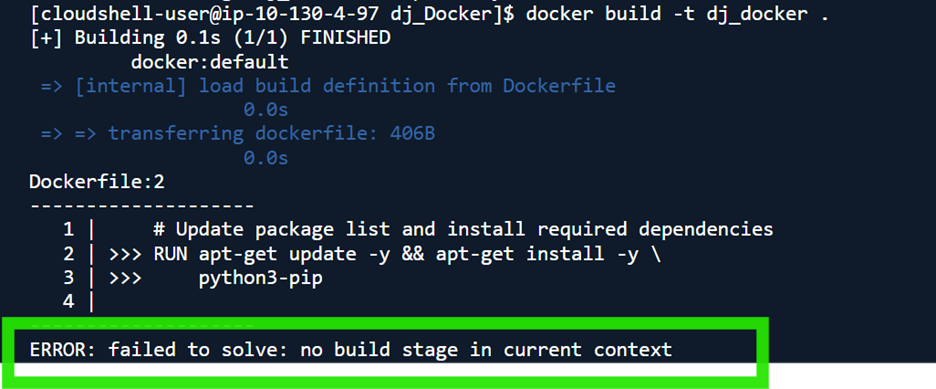
So I added the missing FROM
- re-run docker build -t python_boto3_image .
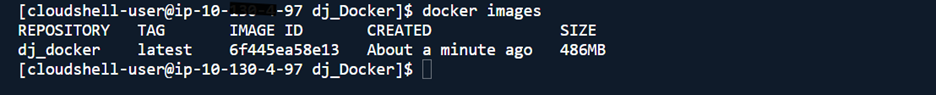
- Go back to the running image: docker image
Step 3 – Download GitHub Repositories
- Create or find 3 repositories on GitHub
- Clone these three repositories locally:
git clone <GitHub_Repo_URL>
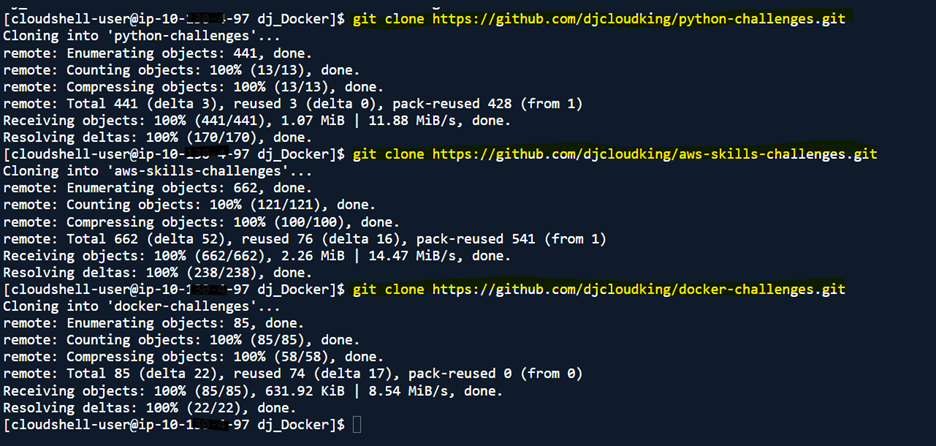
- Verify if the 3 repositories are in your folder
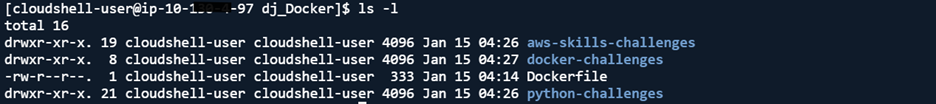
Step 4. Create Ubuntu Containers with Bind Mounts
- Run containers with bind mounts for each repository directory:
docker run -d -t –name <containerName> -v “$(pwd)/<repoDir>:/dj_Docker” ubuntu
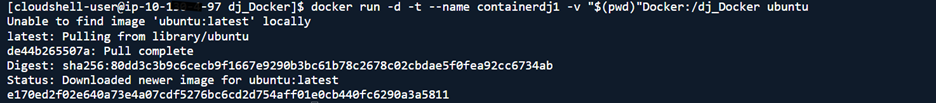

- List active containers:
docker ps

Step 5. Inspect and Verify Bind Mounts
- Inspect bind mounts: docker container inspect <containerName>
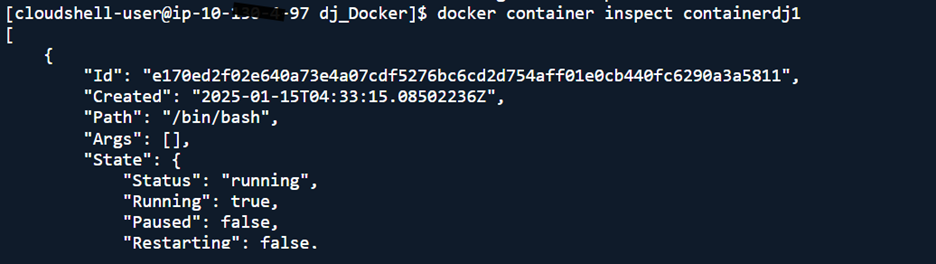
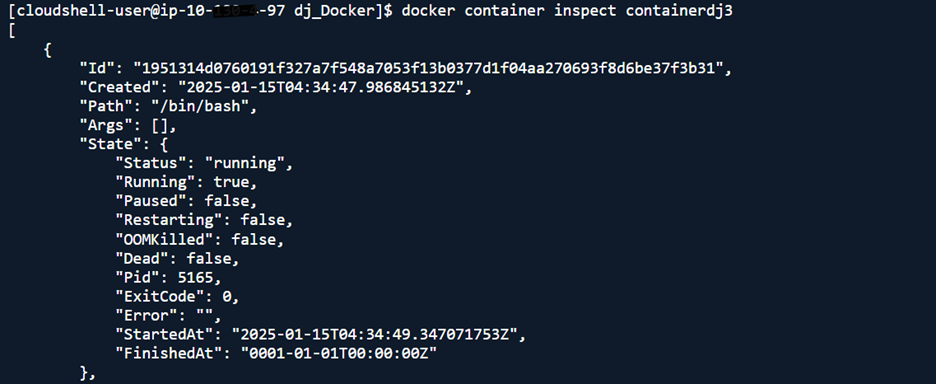
- Access each container to verify: docker exec -it <containerName> bash
- Exit each container before accessing the next: exit
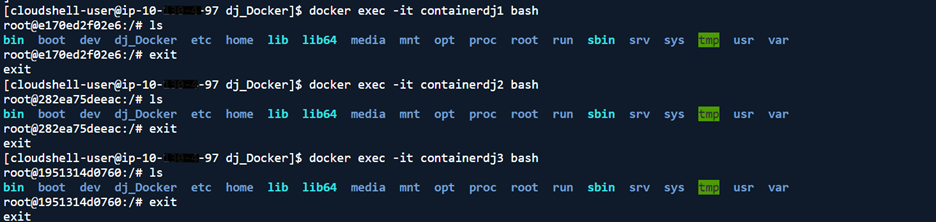
We successfully created Docker containers for Python projects, configured bind mounts, logged into containers.
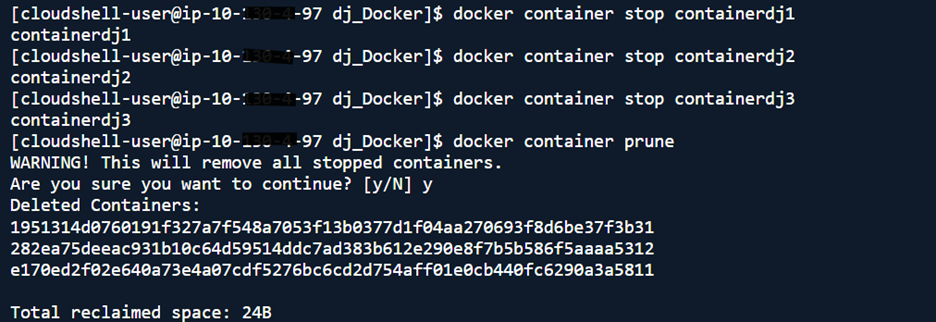
If time to cleaned up our resources.
- Stop and remove containers: docker container stop <containerName>
docker container prune
Thank you for reading and/or following along! Leave us a comment, Share & Follow. Please stay tuned for all my upcoming projects.


Leave a Reply