Terraform isn’t just for big, end-to-end projects. As a Cloud or DevOps engineer, you’ll often work on smaller but critical tasks like creating and connecting a database server, setting up a security group, or running a bootstrap script on a web server.
For beginners, these tasks are great practice because they reflect what you’ll do in enterprise environments. I created a step-by-step tutorial to walk you through some of the daily tasks you might encounter.
This tutorial walks you through deploying a simple AWS setup using Terraform. You’ll create a database server, a web server with a fixed IP address, configure security groups, and run a bootstrap script on the web server.
Scenario
As the DevOps engineer on duty, your supervisor has asked you to complete the following tasks:
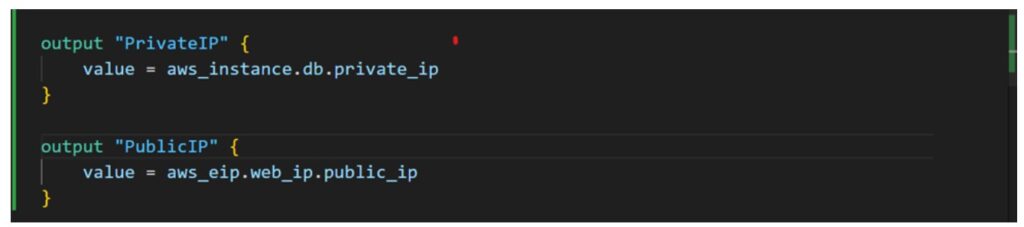
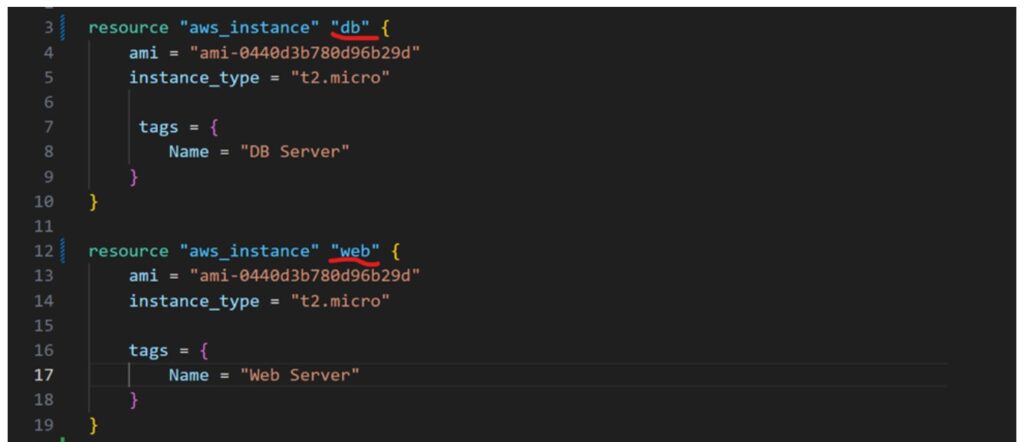
- Create a database (DB) server and output its private IP.
- Create a web server with a fixed public IP.
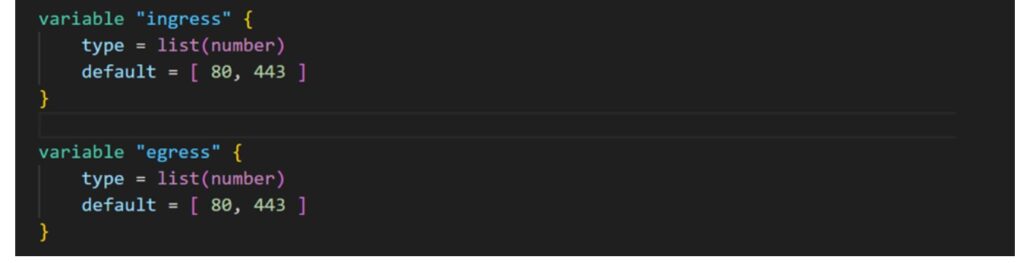
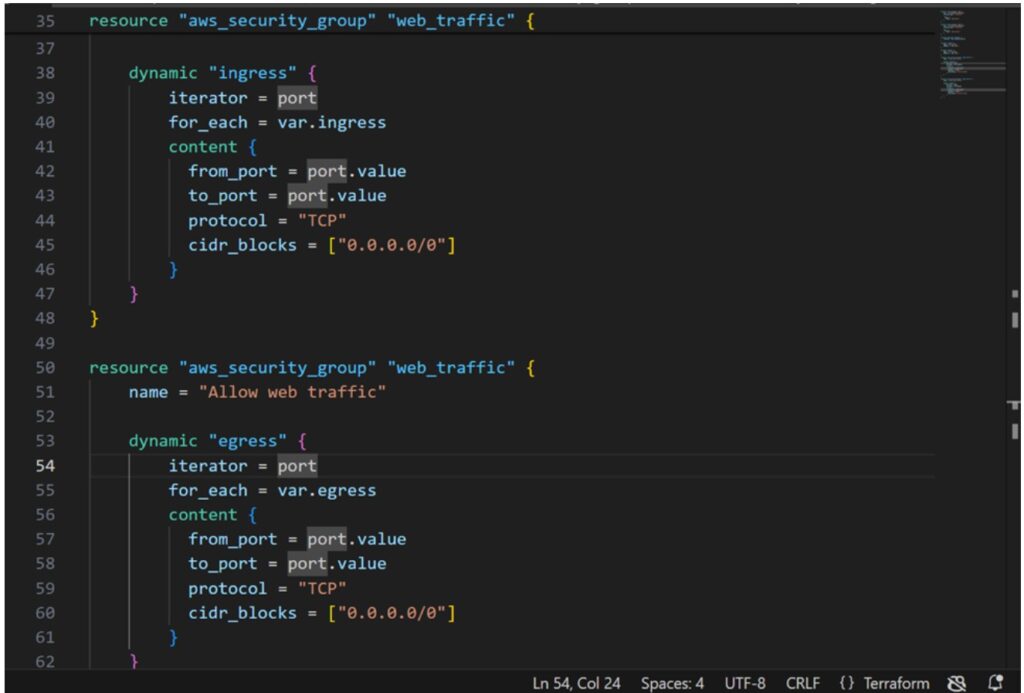
- Create a security group for the web server, opening ports 80 (HTTP) and 443 (HTTPS).
- Run a provided bootstrap script on the web server.
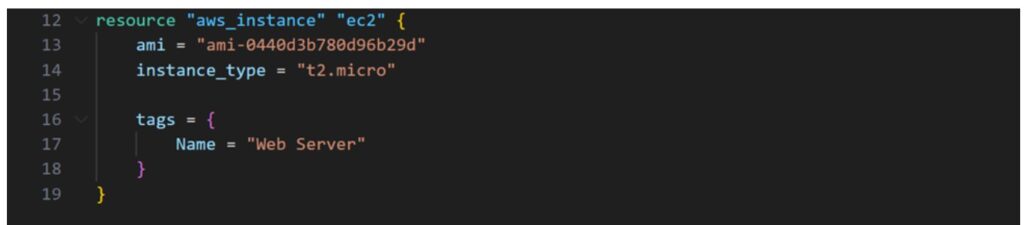
Step 1: Create a Database Server and Output Its Private IP
- Create the project folders
- Open VS Code.
- Create a folder named WebServer.
- Inside it, create another folder named dbserverchallenge.
You’ll find all the code source for this tutorial in this repo folder: Web Server.

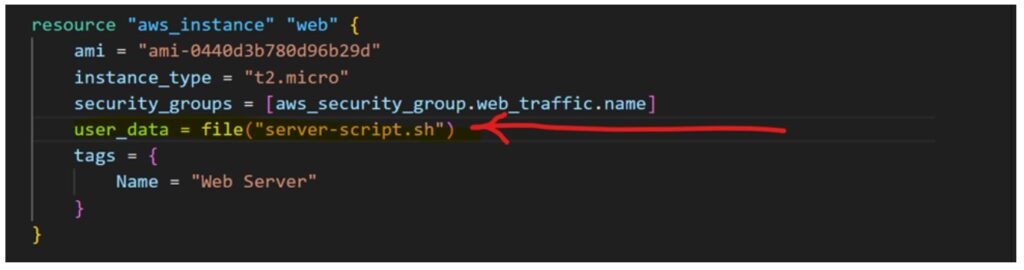
If you run into issues with the user_data script:
-
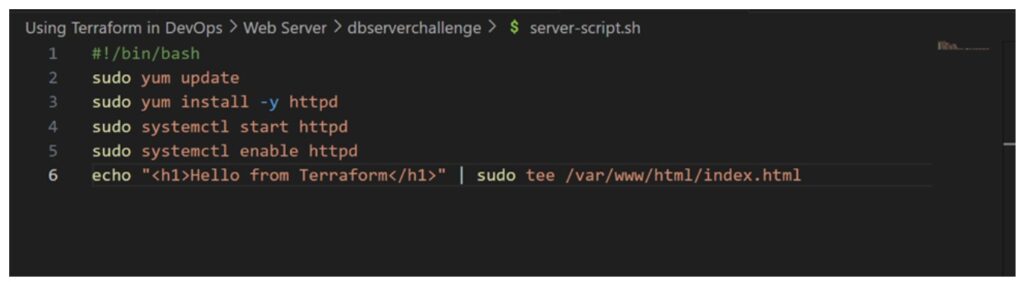
Double-check that the
server-script.shfile has executable permissions:chmod +x server-script.sh
-
Verify that the file path matches what you reference in Terraform.
You’ve successfully:
- Built a database server and web server using Terraform.
- Attached a fixed IP to the web server.
- Configured security groups for secure traffic.
- Automated server setup with a bootstrap script.


Leave a Reply